Discover The Causes and Ways To Identify Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a common type of skin cancer that develops in the squamous cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Understanding its causes and learning how to identify it early are crucial steps in preventing and treating this potentially serious condition. This article will explore the primary causes of squamous cell carcinoma, its typical symptoms, and where it commonly appears on the body, providing you with valuable information to recognize and address this skin cancer effectively.
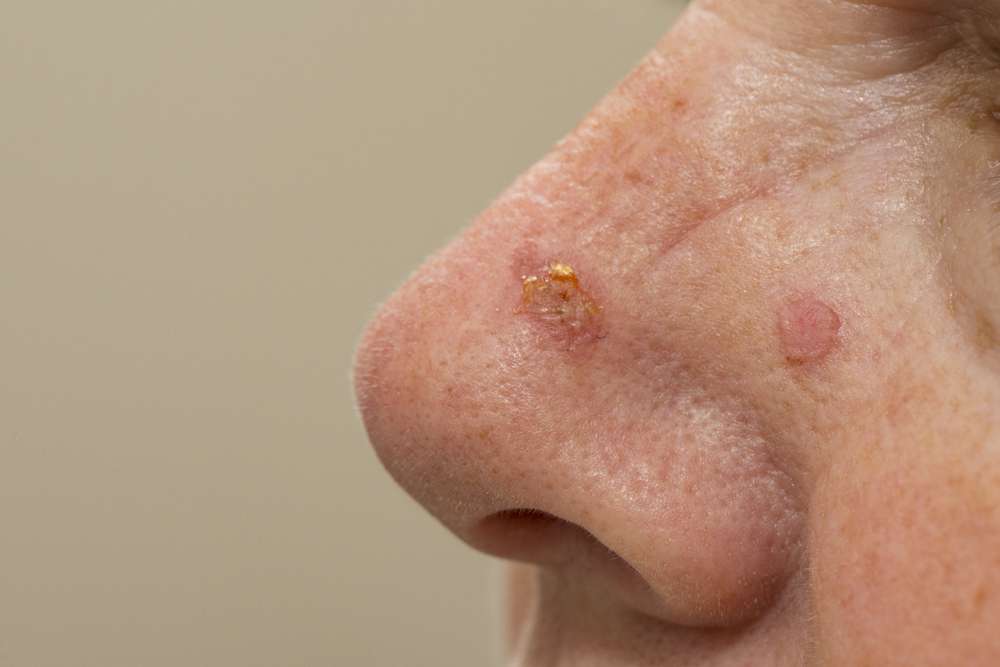
What are the primary causes of squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma primarily develops due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. This exposure can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of cancerous tumors. Other factors that can contribute to the development of SCC include:
-
Fair skin: People with light skin, blonde or red hair, and blue, green, or gray eyes are more susceptible to UV damage.
-
Age: The risk of developing SCC increases with age, as cumulative sun exposure builds up over time.
-
Weakened immune system: Conditions or medications that suppress the immune system can increase the risk of skin cancer.
-
Chronic skin inflammation or injury: Long-standing skin issues, such as scars or ulcers, can sometimes develop into SCC.
-
Exposure to certain chemicals: Arsenic and some industrial compounds may increase the risk of SCC.
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Certain strains of HPV can contribute to the development of SCC, particularly in the genital and anal regions.
How can you recognize the signs of squamous cell carcinoma?
Identifying squamous cell carcinoma early is crucial for successful treatment. While SCC can vary in appearance, there are several common signs to watch for:
-
A firm, red nodule: This is often the most noticeable sign of SCC, appearing as a raised bump on the skin.
-
A flat, scaly patch: Some SCCs may present as a rough, reddish patch that doesn’t heal.
-
A sore that doesn’t heal: If you have a persistent sore that bleeds easily and doesn’t heal within a few weeks, it could be a sign of SCC.
-
A growth with a crusted surface: SCC can sometimes appear as a wart-like growth with a rough, scaly surface.
-
An area of skin that feels tight or stretched: This sensation may be accompanied by itching or tenderness.
If you notice any of these signs, especially in areas frequently exposed to the sun, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist for a professional evaluation.
What are the typical symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma?
While the visual signs of squamous cell carcinoma are often the most apparent, there are other symptoms to be aware of:
-
Persistent itching: The affected area may be itchy, although this isn’t always present.
-
Pain or tenderness: Some SCCs can be painful or sensitive to touch, particularly as they grow larger.
-
Bleeding: The lesion may bleed easily, especially when scratched or irritated.
-
Changes in existing moles or skin growths: If you notice changes in size, color, or texture of existing skin marks, it could be a sign of SCC.
-
Numbness or tingling: In rare cases, SCC can affect nearby nerves, causing unusual sensations in the surrounding skin.
It’s important to note that not all squamous cell carcinomas will exhibit these symptoms. Regular self-examinations and annual skin checks by a dermatologist are crucial for early detection.
Where on the body does squamous cell carcinoma typically appear?
Squamous cell carcinoma most commonly develops on areas of the body that receive frequent sun exposure. These areas include:
-
Face: Particularly the nose, cheeks, ears, and lips
-
Scalp: Especially in individuals with thinning hair or bald spots
-
Neck: Both the front and back of the neck are susceptible
-
Hands: The backs of the hands often receive significant sun exposure
-
Arms: Particularly the forearms and upper arms
-
Shoulders: A common area for sun damage
-
Legs: Especially in women who frequently wear skirts or shorts
While these are the most common locations, it’s important to remember that SCC can develop anywhere on the body, including areas that don’t receive direct sunlight. Less common locations include the genital area, inside the mouth, and on the soles of the feet.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and recognizing the signs of squamous cell carcinoma is crucial for early detection and successful treatment. By being aware of the risk factors, typical symptoms, and common locations of SCC, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin and seek medical attention when necessary. Remember to perform regular self-examinations, protect your skin from excessive sun exposure, and consult a dermatologist if you notice any suspicious changes in your skin.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




