Finding the Right Glucose Monitor for Your Health Needs
For individuals managing diabetes or those concerned about their blood sugar levels, a reliable glucose monitor is an essential tool. These devices provide valuable insights into your body's glucose levels, helping you make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. This article will guide you through the process of selecting the most suitable glucose monitor for your specific health needs.
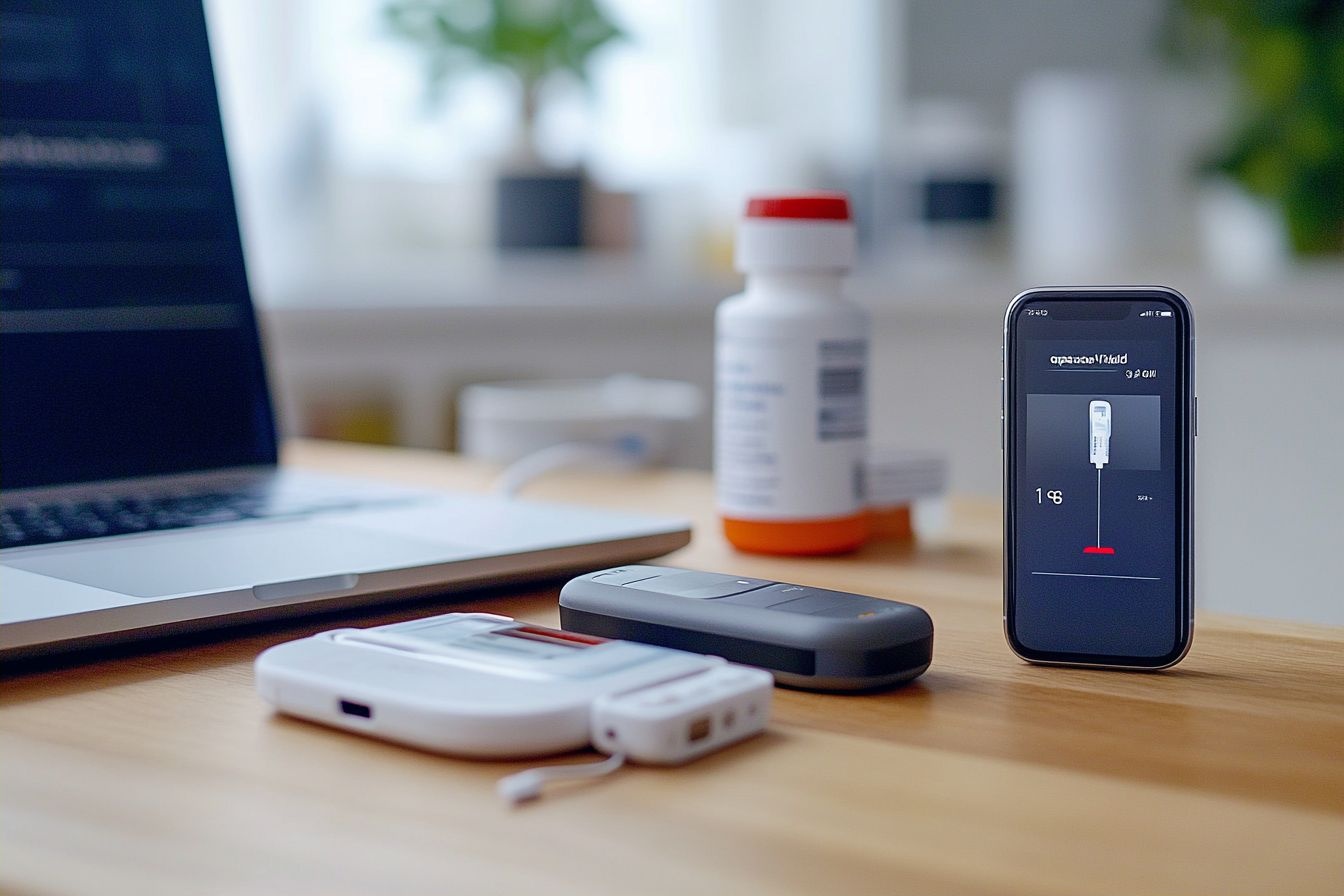

What are the different types of glucose monitors available?
Glucose monitors come in various forms, each catering to different preferences and lifestyles. The most common types include:
-
Traditional Blood Glucose Meters: These require a small blood sample, usually obtained by pricking a fingertip. They provide accurate readings within seconds and are widely used due to their reliability and affordability.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These devices use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid continuously. They provide real-time data and trends, allowing users to track their glucose levels throughout the day and night.
-
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitors: These newer devices aim to measure glucose levels without the need for blood samples or sensor insertion. While promising, their accuracy and availability may vary.
Understanding these options is crucial in determining which type aligns best with your lifestyle and medical needs.
What factors should you consider when choosing a glucose monitor?
Selecting the right glucose monitor involves weighing several important factors:
-
Accuracy: Look for monitors that meet or exceed ISO 15197:2013 standards for accuracy.
-
Ease of Use: Consider the size of the display, the simplicity of the interface, and how easy it is to obtain and interpret results.
-
Testing Frequency: If you need to test multiple times a day, a device with a larger memory capacity and data management features may be beneficial.
-
Lifestyle Compatibility: For active individuals or those who travel frequently, a compact and portable device might be preferable.
-
Additional Features: Some monitors offer Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone integration, or the ability to track other health metrics.
-
Insurance Coverage: Check with your insurance provider to see which devices are covered under your plan.
By carefully considering these factors, you can narrow down your options to find a glucose monitor that best suits your daily routine and health management needs.
How much do glucose monitors typically cost?
The cost of glucose monitors can vary significantly depending on the type, brand, and features. Here’s a general overview of pricing:
Traditional Blood Glucose Meters:
-
Basic models: $10 - $50
-
Advanced models with additional features: $50 - $150
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems:
-
Initial cost (including transmitter and receiver): $1,000 - $1,500
-
Ongoing costs for sensors: $300 - $500 per month
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitors:
- Prices can range from $100 to over $1,000, depending on the technology used
It’s important to note that these prices don’t include the cost of test strips, lancets, or other consumables required for ongoing use.
| Type of Monitor | Price Range | Additional Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Blood Glucose Meter | $10 - $50 | Test strips, lancets |
| Advanced Blood Glucose Meter | $50 - $150 | Test strips, lancets |
| CGM System | $1,000 - $1,500 | Sensors ($300 - $500/month) |
| Non-Invasive Monitor | $100 - $1,000+ | Varies by model |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
When considering the cost of a glucose monitor, it’s crucial to factor in both the initial purchase price and the ongoing expenses for supplies. Some insurance plans may cover part or all of these costs, so be sure to check with your provider for specific coverage details.
How can you ensure accurate readings from your glucose monitor?
To maintain the accuracy and reliability of your glucose monitor:
-
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully for use and maintenance.
-
Wash your hands thoroughly before testing to avoid contamination.
-
Use fresh test strips and check their expiration date.
-
Calibrate your device regularly if required (especially for CGM systems).
-
Store your monitor and supplies in a cool, dry place.
-
Compare your home readings with lab results periodically to ensure accuracy.
By following these steps, you can help ensure that your glucose monitor provides consistent and reliable results, enabling you to make informed decisions about your health management.
Choosing the right glucose monitor is a personal decision that depends on your individual health needs, lifestyle, and preferences. By understanding the types of monitors available, considering key factors, and being aware of the associated costs, you can make an informed choice that supports your diabetes management or blood sugar monitoring goals. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate glucose monitoring solution for your specific situation.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.