Explore Which Foods Are Good for Diabetics and Which Should Be Avoided
Managing diabetes effectively requires careful attention to diet and nutrition. What you eat directly impacts blood sugar levels, making food choices a critical aspect of diabetes management. Understanding which foods can help maintain stable blood glucose levels and which might cause dangerous spikes is essential knowledge for anyone living with diabetes or supporting someone with this condition.
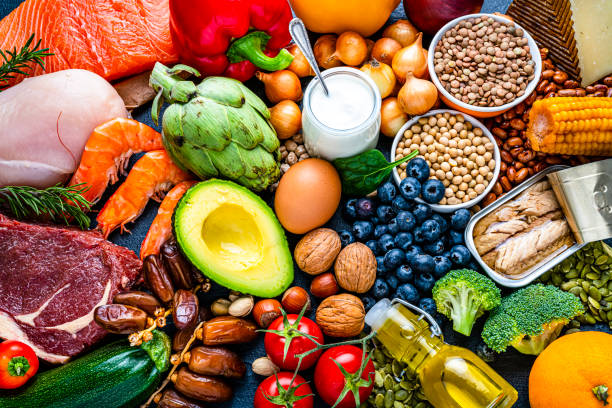

Foods Are Good for Diabetics
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetics, and certain foods can help achieve this goal. Non-starchy vegetables top the list of diabetes-friendly options. Broccoli, spinach, kale, cauliflower, and bell peppers are excellent choices as they’re high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals while having minimal impact on blood sugar. These vegetables can be consumed in generous portions without worry.
Whole grains provide a better alternative to refined carbohydrates. Foods like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley contain fiber that slows digestion and prevents rapid blood sugar spikes. The American Diabetes Association recommends that at least half of grain consumption should come from whole grains rather than refined options.
Lean proteins are another essential food group for diabetics. Chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, tofu, and legumes provide necessary nutrients without affecting blood sugar significantly. Proteins help you feel full longer and can prevent overeating of carbohydrate-rich foods. Including protein with each meal can also help moderate post-meal blood sugar rises.
Foods To Avoid for Diabetics
Certain foods can cause dangerous blood sugar spikes and should be limited or avoided entirely. Refined carbohydrates and sugary foods rank highest on this list. White bread, white rice, regular pasta, pastries, candy, and sugary sodas can cause rapid blood sugar elevation and should be minimized in a diabetic diet.
Processed foods often contain hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive sodium. These ingredients not only impact blood sugar but also contribute to other health issues like high blood pressure, which can complicate diabetes management. Reading nutrition labels carefully can help identify these hidden dangers in packaged foods.
Full-fat dairy products and fatty cuts of meat contain saturated fats that can worsen insulin resistance over time. While some fat is necessary in a healthy diet, it’s best to choose healthier fat sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These healthy fats can actually improve insulin sensitivity when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
What Food Can Diabetics Eat Freely?
While no food should be consumed without some awareness of portion size, certain options can be enjoyed more liberally by people with diabetes. Non-starchy vegetables like cucumber, celery, leafy greens, zucchini, and bell peppers are extremely low in carbohydrates and calories while being rich in essential nutrients and fiber. These can be eaten in larger quantities without significant blood sugar impact.
Water and unsweetened beverages should be the primary drinks for diabetics. Water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee won’t raise blood sugar levels. Adding herbs like mint or slices of lemon can enhance flavor without adding carbohydrates. Staying well-hydrated also helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports overall health.
Sugar-free gelatin, pickles (watch sodium content), and plain popcorn (without butter or sugar) can serve as snacks that won’t significantly impact blood glucose. However, even with “free” foods, moderation remains important since consuming very large quantities of anything can potentially affect blood sugar, especially when combined with other foods.
Healthy Foods For Diabetics
Fatty fish deserves special attention in a diabetic diet plan. Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that help reduce inflammation and improve heart health – important benefits since diabetes increases cardiovascular risk. The American Diabetes Association recommends eating fish at least twice weekly.
Beans and legumes provide a powerful combination of protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates. These nutrients work together to provide sustained energy without causing blood sugar spikes. Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans can be incorporated into soups, salads, and main dishes to increase nutritional value while helping manage glucose levels.
Berries offer sweetness with fewer carbohydrates than most fruits. Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with antioxidants and fiber while having a lower glycemic impact than many other fruits. A small serving of berries can satisfy sweet cravings without causing significant blood sugar elevation.
Healthy Snacks for Diabetics
Strategic snacking can help diabetics maintain stable blood sugar between meals. A small handful of nuts (about 1 ounce) provides healthy fats, protein, and fiber that help prevent hunger without spiking glucose levels. Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are particularly beneficial options, though portion control remains important due to their calorie density.
Greek yogurt with a sprinkle of cinnamon makes an excellent diabetic-friendly snack. The protein content helps with satiety while having minimal effect on blood sugar, and cinnamon may help improve insulin sensitivity. Choosing plain, unsweetened yogurt and adding your own fruit allows control over added sugars.
Hummus with raw vegetables combines protein and fiber from the chickpeas with the nutrients and crunch of vegetables like carrots, celery, and bell peppers. This satisfying combination provides steady energy while keeping blood sugar stable between meals. The fiber in both components slows digestion and prevents rapid glucose fluctuations.
Managing diabetes through diet doesn’t mean eliminating enjoyment from eating. By understanding which foods support stable blood sugar and which cause problematic spikes, people with diabetes can create meal plans that are both nutritious and satisfying. Working with healthcare providers and dietitians can further personalize dietary approaches based on individual needs and preferences.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.