5 Early Skin Cancer Signs That Might Help In Early Detection
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Recognizing the early signs of skin cancer can significantly improve outcomes and potentially save lives. This article will explore five key indicators that might help in the early detection of skin cancer, including melanoma, the most dangerous form.
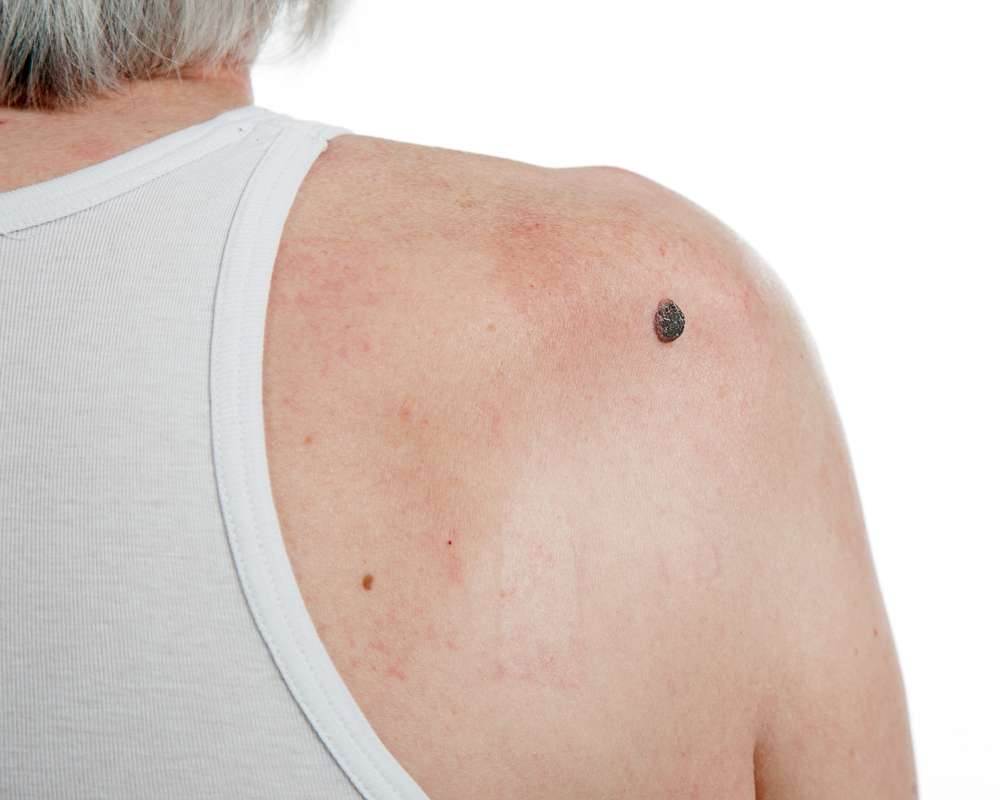
What are the first signs of skin cancer to look out for?
The first signs of skin cancer often appear as changes in the skin’s appearance. These can include:
-
New moles or growths: Any new spot on the skin, especially if it appears after age 21, should be examined.
-
Changes in existing moles: Look for changes in size, shape, or color of existing moles.
-
Asymmetry: If you draw an imaginary line through a mole and the two halves don’t match, it could be a warning sign.
-
Border irregularity: Benign moles typically have smooth, even borders. Jagged or blurred edges may indicate skin cancer.
-
Color variations: Multiple colors or uneven distribution of color within a single mole can be concerning.
How can you detect skin cancer early at home?
Regular self-examination is key to detecting skin cancer early. Here’s how you can perform a thorough skin check at home:
-
Use a full-length mirror and a hand mirror to examine your entire body, including hard-to-see areas.
-
Check all areas of your skin, including between toes, under nails, and on your scalp.
-
Look for the “ABCDE” signs: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color changes, Diameter larger than 6mm, and Evolving size, shape, or color.
-
Take photos of suspicious moles or marks to track changes over time.
-
Perform these checks monthly, and record any changes you notice.
When should you visit a doctor for a skin cancer check?
It’s important to consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider if you notice any of the following:
-
A mole or spot that matches any of the ABCDE criteria mentioned earlier.
-
Any new growth, especially if it appears suddenly or continues to grow.
-
A sore that doesn’t heal within two weeks.
-
A mole that itches, bleeds, or becomes painful.
-
Any significant changes in existing moles or skin marks.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice if you’re unsure about any skin changes. Early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in outcomes.
How is skin cancer formed, and what factors contribute to its development?
Skin cancer forms when mutations occur in the DNA of skin cells, usually as a result of damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. These mutations cause cells to grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a mass of cancer cells. Several factors contribute to skin cancer development:
-
UV exposure: Both natural sunlight and artificial sources like tanning beds can damage skin cells.
-
Fair skin: People with lighter skin tones are more susceptible to UV damage.
-
History of sunburns: Severe sunburns, especially in childhood, increase skin cancer risk.
-
Family history: Genetic factors can play a role in skin cancer susceptibility.
-
Weakened immune system: Certain medical conditions or treatments can increase vulnerability to skin cancer.
What unique insights about skin cancer are relevant to residents of the United States?
In the United States, skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, with over 5 million cases diagnosed annually. Some unique insights for U.S. residents include:
-
Higher rates in southern states: Due to increased sun exposure, southern states tend to have higher skin cancer rates.
-
Rising rates among young adults: Melanoma rates are increasing faster in young adults, particularly women.
-
Workplace risks: Outdoor workers in industries like agriculture and construction face higher skin cancer risks.
-
Racial disparities: While skin cancer is less common in people of color, it’s often diagnosed at later stages, leading to poorer outcomes.
-
Tanning bed regulations: Many states have implemented laws restricting tanning bed use for minors, aiming to reduce skin cancer risk.
What are the most effective prevention strategies for skin cancer?
Preventing skin cancer involves protecting your skin from UV damage and maintaining regular skin checks. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
-
Wear protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
-
Seek shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm).
-
Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps, which can significantly increase skin cancer risk.
-
Perform regular self-examinations and schedule annual skin checks with a dermatologist.
Skin cancer is a serious concern, but with vigilance and proper precautions, it can often be detected early and treated effectively. By understanding the early signs of skin cancer and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect your skin health. Remember, when in doubt about any skin changes, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




